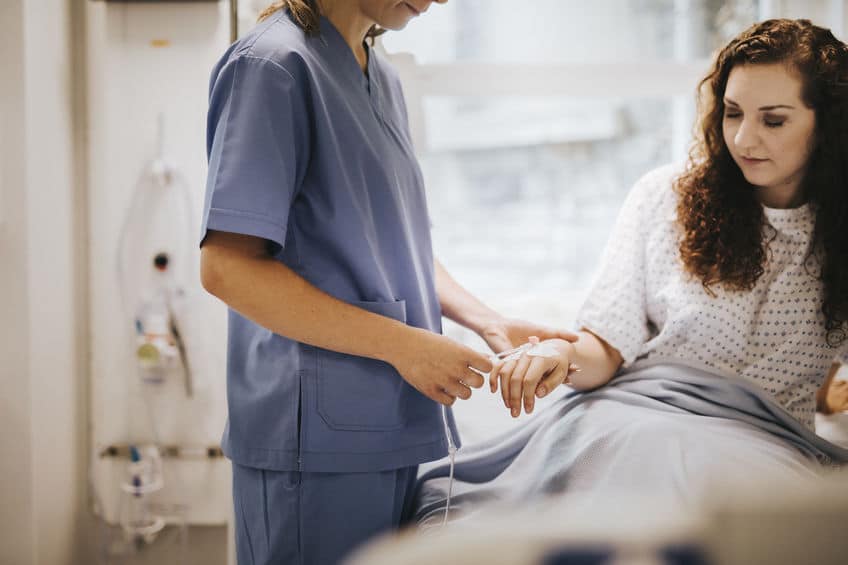
Chelation therapy is a treatment used in alternative medicine. It’s based on the process of chelation, where chemicals are used to remove heavy metals and other substances from the body. Chelation therapy was originally used to treat conditions like lead poisoning, but is now claimed to protect against heart disease and other major health problems.
In chelation therapy, a chemical substance is introduced into the body through an intravenous (IV) drip. Once it enters the bloodstream, the chemical substance binds to certain molecules (such as metals or minerals) and then removes those molecules from the body. According to proponents of chelation therapy, eliminating excess or toxic metals or minerals from the body can enhance your health and help to fight disease.
It should be noted that the only FDA-approved chelating agents are available on a prescription basis only. These agents are approved for use only in specific circumstances, such as in the case of lead poisoning or iron overload.
Uses for Chelation Therapy
Chelation therapy is said to aid in the treatment of atherosclerosis (i.e., hardening of the arteries). Since calcium deposits are found in artery-clogging plaques, it’s thought that using chelation therapy to remove calcium deposits can restore healthy blood flow in the arteries.
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Angina
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Multiple sclerosis
- Peripheral artery disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Band Keratopathy
Side Effects & Safety Concerns
Side effects commonly associated with chelation therapy include diarrhea, headache, high blood pressure, loose stools, low blood sugar, nausea, poor appetite, skin rash, and vomiting. In some cases, chelation therapy may trigger serious side effects such as kidney damage and abnormally low blood levels of calcium.6
There’s also some concern that chelation therapy could remove calcium from healthy bones and other tissues. Children, pregnant women, and people with heart or kidney failure should not receive chelation therapy.